关键概念
数据关系:分别是 "一对一"、"一对多" 和 "多对多",前俩种分别用线性表和树来存储。
图:"多对多"逻辑关系数据的结构
顶点:图中存储的各个数据元素
边:表示顶点之间的关系
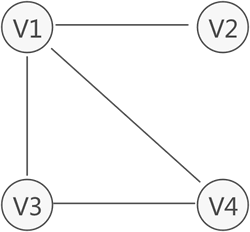
无向图:图中每条边都是无方向的
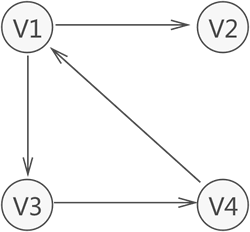
有向图:给图的每条边规定一个方向
子图:指节点集和边集分别是某一图的节点集的子集和边集的子集的图
连通图:图中任意两点都是连通的
路径:无论是无向图还是有向图,从一个顶点到另一顶点途径的所有顶点组成的序列(包含这两个顶点),称为一条路径
回路:如果路径中第一个顶点和最后一个顶点相同,则此路径称为"回路"
参考资料
- 无向图
- 有向图
- 连通图

图的存储结构
存储结构:
- 顺序存储
- 邻接点存储
- 十字链表存储
- 邻接点多重表存储
顺序存储
用数组顺序存储图的顶点和关系。
一维数组存储图的顶点,二维数组存储图的关系。
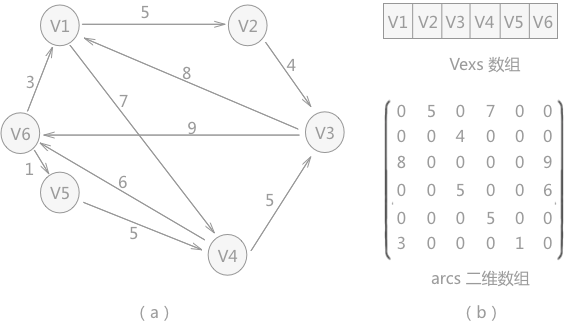
邻接点存储
图中的各个顶点独自建立一个链表,用节点存储该顶点,用链表中其他节点存储各自的临界点。
十字链表存储
十字链表法仅适用于存储有向图和有向网
邻接点多重表存储
邻接多重表仅适用于存储无向图或无向网。
邻接多重表存储无向图的方式,可看作是邻接表和十字链表的结合。
图的遍历
深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)
图:
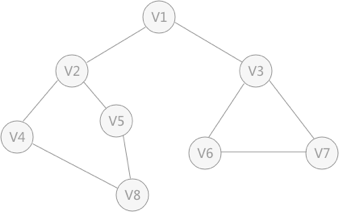
DFS
从图中的一个顶点出发,每次遍历当前访问顶点的临界点,一直到访问的顶点没有未被访问过的临界点为止。
然后采用依次回退的方式,查看来的路上每一个顶点是否有其它未被访问的临界点。
访问完成后,判断图中的顶点是否已经全部遍历完成,如果没有,以未访问的顶点为起始点,重复上述过程
节点遍历顺序:
V1 -> V2 -> V4 -> V8 -> V5 -> V3 -> V6 -> V7
BFS
广度优先搜索类似于树的层次遍历。
从图中的某一顶点出发,遍历每一个顶点时,依次遍历其所有的邻接点,然后再从这些邻接点出发,同样依次访问它们的邻接点。
按照此过程,直到图中所有被访问过的顶点的邻接点都被访问到。
BFS遍历顺序:
V1 -> V2 -> v3 -> V4 -> V5 -> V6 -> V7 -> V8
package main
import "fmt"
type Node struct {
left *Node
right *Node
value string
}
var res [][]string
func main() {
var path []string
e := Node{nil, nil, "5"}
d := Node{nil, nil, "4"}
c := Node{left: nil, right: &e, value: "3"}
b := Node{nil, nil, "6"}
a := Node{left: &c, right: &d, value: "2"}
head := Node{left: &a, right: &b, value: "1"}
BinaryTreePath(&head, path)
fmt.Println(res)
}
func BinaryTreePath(root *Node, path []string) {
path = append(path, root.value)
if root.left == nil && root.right == nil {
res = append(res, path)
}
if root.left != nil {
BinaryTreePath(root.left, path)
}
if root.right != nil {
BinaryTreePath(root.right, path)
}
}
什么是图数据库
图数据库(英语:graph database,GDB[1])是一个使用图结构进行语义查询的数据库,它使用节点、边和属性来表示和存储数据。
NoSQL存储类型:K-V存储、文档存储、列式存储、图存储。
几种常见的图数据库对比
值得关注的图数据库
| 名称 | 版本 | 许可证 | 语言 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neo4j | 3.3.5 (2018-04)[17] | GPLv3 社区版,商业 & AGPLv3 企业和高级版 | Java, NET[需要消歧义], JavaScript, Python, Ruby | 开源,支持ACID,具有用于企业部署的高可用性集群,并附带基于Web的管理工具,包括完整事务支持和可视节点链接图浏览器;可以使用其内置的REST Web API接口从大多数编程语言访问,以及使用官方驱动程序的专有Bolt协议;截至2019年1月最受欢迎的图数据库。[[18]]( |
| JanusGraph | 0.6.1 (2022-01-18)[13] | Apache 2 | Java | 开源、可扩展、在Linux基金会下的分布式图数据库;支持各种存储后端(Cassandra,HBase,Bigtable,BerkeleyDB);[14] 通过与大数据平台(Spark、Giraph、Hadoop)的集成支持全局图数据分析、报告和ETL;通过外部索引存储支持地理、数字范围和全文检索(ElasticSearch、Solr、Lucene)。[15] |
| HugeGraph | v0.10.4(页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) (2019-11-08) | Apache 2 | Java, Gremlin, Python | 百度开源(页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)的分布式图数据库。支持标准的Apache Tinkerpop Gremlin图查询语言,支持属性图,可支持千亿级规模关系数据;支持多种后端存储(Cassandra,HBase,RocksDB,MySQL,PostgreSQL,ScyllaDB);支持各类索引(二级索引、范围索引、全文索引、联合索引,均无需依赖第三方索引库);提供可视化的Web界面,可用于图建模、数据导入、图分析;提供导入工具支持从多种数据源中导入数据到图中,支持的数据源包括:CSV、HDFS、关系型数据库(MySQL、Oracle、SQL Server、PostgreSQL);支持REST接口,并提供10+种通用的图算法;支持与Hadoop、Spark GraphX等大数据系统集成。[[12]]( |
相关资料
Ent 实体框架
官网:https://entgo.io/zh/
entimport: https://entgo.io/zh/blog/2021/10/11/generating-ent-schemas-from-existing-sql-databases
entgrpc: https://entgo.io/docs/grpc-intro
entgql: https://entgo.io/docs/tutorial-todo-gql
entviz: https://entgo.io/zh/blog/2021/08/26/visualizing-your-data-graph-using-entviz
初始化
go mod init <project>
go install entgo.io/ent/cmd/ent@latest
go run entgo.io/ent/cmd/ent init User Class
执行初始化后的目录结构:
--schema
----user.go
----class.go
--generate.go
得到schema定义框架。如下:
// schema/user.go
package schema
import "entgo.io/ent"
// User holds the schema definition for the User entity.
type User struct {
ent.Schema
}
// Fields of the User.
func (User) Fields() []ent.Field {
return nil
}
// Edges of the User.
func (User) Edges() []ent.Edge {
return nil
}
// generate.go
package ent
//go:generate go run -mod=mod entgo.io/ent/cmd/ent generate ./schema
补充实体和边
// schema/user.go
package schema
import (
"entgo.io/ent"
"entgo.io/ent/schema/edge"
"entgo.io/ent/schema/field"
)
// User holds the schema definition for the User entity.
type User struct {
ent.Schema
}
// Fields of the User.
func (User) Fields() []ent.Field {
return []ent.Field{
field.Int("age").
Positive(),
field.String("name").
Default("unknown"),
}
}
// Edges of the User.
func (User) Edges() []ent.Edge {
return []ent.Edge{
edge.To("classes", Class.Type),
}
}
生成代码
go generate ./ent
或者
go generate ./...
创建实体和边数据
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
_ "github.com/mattn/go-sqlite3"
"log"
"test/ent"
"test/ent/class"
"test/ent/user"
)
func main() {
client, err := ent.Open("sqlite3", "file:./ent.db?cache=shared&_fk=1")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed opening connection to sqlite: %v", err)
}
defer client.Close()
// Run the auto migration tool.
if err := client.Schema.Create(context.Background()); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed creating schema resources: %v", err)
}
//_, err = CreateUser(context.Background(), client)
//if err != nil {
// log.Fatalf("failed creating schema resources: %v", err)
//}
//u, err := QueryUser(context.Background(), client)
//if err != nil {
// log.Fatalf("failed creating schema resources: %v", err)
//}
//_ = QueryClasses(context.Background(), u)
//创建俩个class,然后创建一个用户关联这俩个class
_, err = CreateClasses(context.Background(), client)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed creating schema resources: %v", err)
}
}
func CreateUser(ctx context.Context, client *ent.Client) (*ent.User, error) {
u, err := client.User.
Create().
SetAge(22).
SetName("868").
Save(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed creating user: %w", err)
}
log.Println("user was created: ", u)
return u, nil
}
func QueryUser(ctx context.Context, client *ent.Client) (*ent.User, error) {
u, err := client.User.
Query().
Where(user.Name("121")).
// `Only` 在 找不到用户 或 找到多于一个用户 时报错,
Only(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed querying user: %w", err)
}
log.Println("user returned: ", u)
return u, nil
}
func CreateClasses(ctx context.Context, client *ent.Client) (*ent.User, error) {
math, err := client.Class.
Create().
SetClassName("math").
SetScore(100).
Save(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed creating class: %w", err)
}
log.Println("class was created: ", math)
chinese, err := client.Class.
Create().
SetClassName("chinese").
SetScore(100).
Save(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed creating car: %w", err)
}
log.Println("car was created: ", chinese)
// 新建一个用户,将两辆车添加到他的名下
a8m, err := client.User.
Create().
SetAge(18).
SetName("121").
AddClasses(math, chinese).
Save(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed creating user: %w", err)
}
log.Println("user was created: ", a8m)
return a8m, nil
}
func QueryClasses(ctx context.Context, a8m *ent.User) error {
cars, err := a8m.QueryClasses().All(ctx)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed querying user cars: %w", err)
}
log.Println("returned cars:", cars)
// What about filtering specific cars.
ford, err := a8m.QueryClasses().
Where(class.ClassName("math")).
Only(ctx)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed querying user cars: %w", err)
}
log.Println(ford)
return nil
}
实体和关系在Golang数据结构中的体现
// User is the model entity for the User schema.
type User struct {
config `json:"-"`
// ID of the ent.
ID int `json:"id,omitempty"`
// Age holds the value of the "age" field.
Age int `json:"age,omitempty"`
// Name holds the value of the "name" field.
Name string `json:"name,omitempty"`
// Edges holds the relations/edges for other nodes in the graph.
// The values are being populated by the UserQuery when eager-loading is set.
Edges UserEdges `json:"edges"`
}
// UserEdges holds the relations/edges for other nodes in the graph.
type UserEdges struct {
// Classes holds the value of the classes edge.
Classes []*Class `json:"classes,omitempty"`
// loadedTypes holds the information for reporting if a
// type was loaded (or requested) in eager-loading or not.
loadedTypes [1]bool
}
// Class is the model entity for the Class schema.
type Class struct {
config `json:"-"`
// ID of the ent.
ID int `json:"id,omitempty"`
// ClassName holds the value of the "class_name" field.
ClassName string `json:"class_name,omitempty"`
// Score holds the value of the "score" field.
Score int64 `json:"score,omitempty"`
user_classes *int
}
实体和边在关系型数据库表中的体现
表:users
| id | age | name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | a8m |
| 2 | 22 | 868 |
| 5 | 18 | 121 |
表:classes
| id | class_name | score | user_classes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | math | 100 | 5 |
| 8 | chinese | 100 | 5 |
TODO:关于其他形式的边的存储结构待补充
参考资料
模板解析
ent的init代码是如何学初始化的?
定义模板
// ./tpl/schema.tpl
package schema
import (
gint "gitee.com/wennmu/gint.git/cmd"
)
type {{ .schemaName }} struct {
gint.Schema
}
func ({{ .schemaName }}) Fields() []gint.Field {
return nil
}
func ({{ .schemaName }}) Edges() []gint.Edge {
// Not currently supported
return nil
}
生成Go文件
schemaDir 为 ./schema
func initSchema(args []string) {
for _, schemaName := range args {
tmpl, err := template.ParseFiles("./tpl/schema.tpl")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
genFile := schemaDir + "/" + strings.ToLower(schemaName) + ".go"
f, err := os.Create(genFile)
defer f.Close()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
err = tmpl.Execute(f, map[string]string{
"schemaName": schemaName,
})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
}
用模板生成的Go文件
package schema
import (
gint "gitee.com/wennmu/gint.git/cmd"
)
type User struct {
gint.Schema
}
func (User) Fields() []gint.Field {
return nil
}
func (User) Edges() []gint.Edge {
// Not currently supported
return nil
}
参考资料
Go文件解析
实际上,ent的generate指的是entc,即ent codegen.
解析Go包,获取实体(即schema)
这里使用了 golang.org/x/tools/go/packages用来校验和分析Go包。
// 从包路径中解析出schema的实体名称
func Generate(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
cfg := &packages.Config{Mode: packages.NeedName | packages.NeedTypes | packages.NeedTypesInfo | packages.NeedModule,}
// 加载要解析的Go包
pkgs, err := packages.Load(cfg, args[0], entInterface.PkgPath())
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "load: %v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
entPkg, pkg := pkgs[0], pkgs[1]
if len(pkg.Errors) != 0 {
log.Println(pkg.Errors[0])
}
if pkgs[0].PkgPath != entInterface.PkgPath() {
entPkg, pkg = pkgs[1], pkgs[0]
}
var names []string
//entInterface.Name() 反射类型名称
//entPkg.Types.Scope().Lookup(entInterface.Name()) 从包的类型中找到给定名称的类型,返回其对象
//.Type().Underlying() 对象类型的基础类型
//(*types.Interface) 转为接口类型
iface := entPkg.Types.Scope().Lookup(entInterface.Name()).Type().Underlying().(*types.Interface)
//pkg.TypesInfo提供有关包的语法树的类型信息
//pkg.TypesInfo.Defs 对象类型的定义信息
//k ast.ident
//type Ident struct {
// NamePos token.Pos // 标识符的位置
// Name string // 标识符的名称
// Obj *Object // 所表示的对象; or nil
//}
//v obj
for k, v := range pkg.TypesInfo.Defs {
//做一些必要的校验
typ, ok := v.(*types.TypeName)
//IsExported id是否是大写开头
//types.Implements 第一参数是否实现了第二参数
if !ok || !k.IsExported() || !types.Implements(typ.Type(), iface) {
continue
}
//一个类型的声明
spec, ok := k.Obj.Decl.(*ast.TypeSpec)
if !ok {
fmt.Errorf("invalid declaration %T for %s", k.Obj.Decl, k.Name)
}
// ast.StructType 结构体类型声明
if _, ok := spec.Type.(*ast.StructType); !ok {
fmt.Errorf("invalid spec type %T for %s", spec.Type, k.Name)
}
//获取到schema的名称
names = append(names, k.Name)
}
fmt.Println(names)
fmt.Println(pkg.PkgPath)
}
//输出:
//[Link User]
//gitee.com/wennmu/gint.git/gint/schema
参考资料
- go/packages - 用来校验和分析Go包。
- go/ast - 用来表示Go包的语法树的类型。
代码生成过程分析
Schema抽象类型
首先需要关注俩个重要的点:Schema的抽象数据类型,Graph的抽象数据类型。这俩者分别存储了Schema的定义和Graph生成的定义。
Schema的抽象数据类型
type Schema struct {
Name string `json:"name,omitempty"`
Config ent.Config `json:"config,omitempty"`
Edges []*Edge `json:"edges,omitempty"`
Fields []*Field `json:"fields,omitempty"`
Indexes []*Index `json:"indexes,omitempty"`
Hooks []*Position `json:"hooks,omitempty"`
Policy []*Position `json:"policy,omitempty"`
Annotations map[string]interface{} `json:"annotations,omitempty"`
}
Graph的抽象数据类型
type (
// The Config holds the global codegen configuration to be
// shared between all generated nodes.
Config struct {
// Schema 保存用户 entschema 的 Go 包路径。
// For example, "<project>/ent/schema".
Schema string
// Target 定义保存生成代码的目标目录的文件路径。例如,“.projectent”。
//
// By default, 'ent generate ./ent/schema' uses './ent' as a
// target directory.
Target string
// Package 定义了上面提到的目标目录的 Go 包路径。例如,“github.comorgprojectent”。
//
// By default, for schema package named "<project>/ent/schema",
// 'ent generate' uses "<project>/ent" as a default package.
Package string
// Header allows users to provides an optional header signature for
// the generated files. It defaults to the standard 'go generate'
// format: '// Code generated by entc, DO NOT EDIT.'.
Header string
// Storage configuration for the codegen. Defaults to sql.
Storage *Storage
// IDType 指定 codegen 中 id 字段的类型。支持的类型是 string 和 int,这也是默认值。
IDType *field.TypeInfo
// Templates specifies a list of alternative templates to execute or
// to override the default. If nil, the default template is used.
//
// Note that, additional templates are executed on the Graph object and
// the execution output is stored in a file derived by the template name.
Templates []*Template
// Features defines a list of additional features to add to the codegen phase.
// For example, the PrivacyFeature.
Features []Feature
// Hooks holds an optional list of Hooks to apply on the graph before/after the code-generation.
Hooks []Hook
// Annotations that are injected to the Config object can be accessed
// globally in all templates. In order to access an annotation from a
// graph template, do the following:
//
// {{- with $.Annotations.GQL }}
// {{/* Annotation usage goes here. */}}
// {{- end }}
//
// For type templates, we access the Config field to access the global
// annotations, and not the type-specific annotation.
//
// {{- with $.Config.Annotations.GQL }}
// {{/* Annotation usage goes here. */}}
// {{- end }}
//
// 请注意,映射是从注释名称(例如“GQL”)到 JSON 解码对象。
Annotations Annotations
}
// Graph holds the nodes/entities of the loaded graph schema. Note that, it doesn't
// hold the edges of the graph. Instead, each Type holds the edges for other Types.
Graph struct {
*Config
// Nodes are list of Go types that mapped to the types in the loaded schema.
Nodes []*Type
// Schemas holds the raw interfaces for the loaded schemas.
Schemas []*load.Schema
}
)
需要注意的是:
- Schema数据类型的实例是通过解析Schema的定义得到的。
- Graph数据类型的实例是通过处理Schema数据,以及结合内外部模板得到的。内部模板是预先内置的,外部模板是用户指定的。
基于模板的生成代码过程分析
大致的流程是这样的:
1. 在系统内部定义了要生成的文件的模板,模板的名称和路径等数据,内置在[]Template数组中,以在生成目标文件的时候调用。
2. 处理Schema数据。在对Schema数据经过一系列的校验、转换等操作后加载到Graph中。比如:将schema转为Graph的节点,转换节点的属性,转换节点的边,转换节点的索引等等。
3. 关键的一步,结合graph和模板,生成目标文件内容。生成的文件路径和文件内容是存在于assets数组中的。当然,在写文件之前,这些全部存在于内存中。
4. 将所有生成的文件落盘。
1. 内置模板
var (
// Templates 保存图形正在生成的文件的模板信息。
Templates = []TypeTemplate{
{
Name: "create",
Format: pkgf("%s_create.go"),
ExtendPatterns: []string{
"dialect/*/create/fields/additional/*",
"dialect/*/create_bulk/fields/additional/*",
},
},
{
Name: "update",
Format: pkgf("%s_update.go"),
},
{
Name: "delete",
Format: pkgf("%s_delete.go"),
},
{
Name: "query",
Format: pkgf("%s_query.go"),
ExtendPatterns: []string{
"dialect/*/query/fields/additional/*",
},
},
{
Name: "model",
Format: pkgf("%s.go"),
},
{
Name: "where",
Format: pkgf("%s/where.go"),
ExtendPatterns: []string{
"where/additional/*",
},
},
{
Name: "meta",
Format: func(t *Type) string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%[1]s/%[1]s.go", t.PackageDir())
},
ExtendPatterns: []string{
"meta/additional/*",
},
},
}
// GraphTemplates保存应用于图表的模板。
GraphTemplates = []GraphTemplate{
{
Name: "base",
Format: "ent.go",
},
{
Name: "client",
Format: "client.go",
ExtendPatterns: []string{
"client/fields/additional/*",
"dialect/*/query/fields/init/*",
},
},
{
Name: "context",
Format: "context.go",
},
{
Name: "tx",
Format: "tx.go",
},
{
Name: "config",
Format: "config.go",
ExtendPatterns: []string{
"dialect/*/config/*/*",
},
},
{
Name: "mutation",
Format: "mutation.go",
},
{
Name: "migrate",
Format: "migrate/migrate.go",
Skip: func(g *Graph) bool { return !g.SupportMigrate() },
},
{
Name: "schema",
Format: "migrate/schema.go",
Skip: func(g *Graph) bool { return !g.SupportMigrate() },
},
{
Name: "predicate",
Format: "predicate/predicate.go",
},
{
Name: "hook",
Format: "hook/hook.go",
},
{
Name: "privacy",
Format: "privacy/privacy.go",
Skip: func(g *Graph) bool {
return !g.featureEnabled(FeaturePrivacy)
},
},
{
Name: "entql",
Format: "entql.go",
Skip: func(g *Graph) bool {
return !g.featureEnabled(FeatureEntQL)
},
},
{
Name: "runtime/ent",
Format: "runtime.go",
},
{
Name: "enttest",
Format: "enttest/enttest.go",
},
{
Name: "runtime/pkg",
Format: "runtime/runtime.go",
},
}
2. 初始化Graph
// NewGraph creates a new Graph for the code generation from the given schema definitions.
// It fails if one of the schemas is invalid.
//从给定的sschema定义中生成图
//如果任意一个图创建失败,则schema是不可用的
func NewGraph(c *Config, schemas ...*load.Schema) (g *Graph, err error) {
defer catch(&err)
//传入配置,schema初始化图
g = &Graph{c, make([]*Type, 0, len(schemas)), schemas}
//遍历shcema,添加为图的节点
for i := range schemas {
g.addNode(schemas[i])
}
//遍历schema添加边
for i := range schemas {
g.addEdges(schemas[i])
}
//处理每个节点的边 变得四种关系
for _, t := range g.Nodes {
check(resolve(t), "resolve %q relations", t.Name)
}
//为每个边创建外键
for _, t := range g.Nodes {
check(t.setupFKs(), "set %q foreign-keys", t.Name)
}
//遍历shcema。添加索引到图中
for i := range schemas {
g.addIndexes(schemas[i])
}
//为了房子冲突,为导入的包定义本地别名
aliases(g)
//执行一下默认的内容,比如进行id类型的设置
g.defaults()
return
}
3. 生成代码
生成代码的核心是运用了text/template包来完成的
//生成模板
b := bytes.NewBuffer(nil)
if err := templates.ExecuteTemplate(b, tmpl.Name, g); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("execute template %q: %w", tmpl.Name, err)
}
4. 写文件,格式化
type (
file struct {
path string
content []byte
}
assets struct {
//涉及的目录存在这里,在写文件之前,创建他们
dirs []string
files []file
}
)
// 在资产中写入文件和目录。
func (a assets) write() error {
for _, dir := range a.dirs {
if err := os.MkdirAll(dir, os.ModePerm); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("create dir %q: %w", dir, err)
}
}
for _, file := range a.files {
if err := os.WriteFile(file.path, file.content, 0644); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("write file %q: %w", file.path, err)
}
}
return nil
}
// format runs "goimports" on all assets.
func (a assets) format() error {
for _, file := range a.files {
path := file.path
src, err := imports.Process(path, file.content, nil)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("format file %s: %w", path, err)
}
if err := os.WriteFile(path, src, 0644); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("write file %s: %w", path, err)
}
}
return nil
}
entimport
主要提供从数据表导入到实体的能力
安装
go run -mod=mod ariga.io/entimport/cmd/entimport -h
执行导入
已经存在数据表:
create table users
(
id integer not null
primary key autoincrement,
age integer not null,
name varchar(255) default 'unknown' not null
);
-- auto-generated definition
create table classes
(
id integer not null
primary key autoincrement,
class_name varchar(255) default 'unknown' not null,
score integer default 0 not null,
user_classes integer
constraint classes_users_classes
references users
on delete set null
);
执行以下命令导入到实体:
go run ariga.io/entimport/cmd/entimport -dsn "root:pass@tcp(localhost:3306)/entimport"
参数说明:
Usage of ~\entimport.exe:
-dsn string
data source name (connection information), for example: //数据源dsn链接,例如:mysql,pgsql
"mysql://user:pass@tcp(localhost:3306)/dbname"
"postgres://user:pass@host:port/dbname"
-schema-path string
output path for ent schema (default "./ent/schema") //输出schema的路径
-tables value
comma-separated list of tables to inspect (all if empty) //指定导出的表明,不指定就是全部表
导出完成的目录结构
├── ent
│ ├── generate.go
│ └── schema
│ ├── class.go
│ └── user.go
导出的实体定义
package schema
import (
"entgo.io/ent"
"entgo.io/ent/schema/edge"
"entgo.io/ent/schema/field"
)
// User holds the schema definition for the User entity.
type User struct {
ent.Schema
}
// Fields of the User.
func (User) Fields() []ent.Field {
return []ent.Field{
field.Int("age").
Positive(),
field.String("name").
Default("unknown"),
}
}
// Edges of the User.
func (User) Edges() []ent.Edge {
return []ent.Edge{
edge.To("classes", Class.Type),
}
}
从ent到grpc
entproto - 通过这个插件,可以包ent实体解析为proto协议
proto-gen-entgrpc - 这是一个protoc的扩展,负责对protoc生成接口的实现。
关于ent对grpc的支持,参阅https://entgo.io/docs/grpc-intro
entgql
通过entc扩展的方式生成ent实体和关系模型
-
GraphQL
API的查询语言,也是使用为数据定义的类型系统执行查询的服务器端运行时。
GraphQL没有绑定到任何特定的数据库或存储引擎,而是由现有代码和数据支持。
-
gqlgen
在Golang构建GraphQL服务器
------------ | GraphQL | ------------ ------------------ | gqlgen Server | ------------------ ----------------------- | 数据存储引擎,存储层 | -----------------------
GraphQL - API查询语言
查询和修改
查询
{
hero {
name
# Queries can have comments!
friends {
name
}
}
}
传递参数
每个字段和嵌套对象都可以传递一组参数
{
human(id: "1000") {
name
height(unit: FOOT)
}
}
定义别名
查询具有不同参数的同一字段时
{
empireHero: hero(episode: EMPIRE) {
name
}
jediHero: hero(episode: JEDI) {
name
}
}
使用片段
片段让您可以构建字段集,然后将它们包含在您需要的查询中。
{
leftComparison: hero(episode: EMPIRE) {
...comparisonFields
}
rightComparison: hero(episode: JEDI) {
...comparisonFields
}
}
fragment comparisonFields on Character {
name
appearsIn
friends {
name
}
}
操作名称
操作类型是查询、变异或订阅
// 操作类型 操作名称
query HeroNameAndFriends {
hero {
name
friends {
name
}
}
}
变量
$episode 是变量,以$开头 可以给变量设置默认值 类型旁边的!表示必须
query HeroNameAndFriends($episode: Episode! = JEDI) {
hero(episode: $episode) {
name
friends {
name
}
}
}
指令
指令可以附加到字段或片段包含 @include(if: Boolean)如果参数为true,则仅在结果中包含此字段。 @skip(if: Boolean)如果参数是true,跳过此字段。
query Hero($episode: Episode, $withFriends: Boolean!) {
hero(episode: $episode) {
name
friends @include(if: $withFriends) {
name
}
}
}
突变
一种修改服务器端数据的方法 查询是并行的,突变的串行的
mutation CreateReviewForEpisode($ep: Episode!, $review: ReviewInput!) {
createReview(episode: $ep, review: $review) {
stars
commentary
}
}
内联片段 TODO
// TODO
gqlgen
阅读官方文档
介绍
类型安全的GraphQL for Go
gqlgen是一个用于构建GraphQL服务器的Go库。
- gqlgen基于模式第一的方法——使用GraphQL模式定义语言定义API。
- gqlgen优先考虑类型安全-你永远不会在这里看到map[string]interface{}。
- gqlgen支持Codegen -我们生成无聊的部分,所以你可以专注于快速构建你的应用程序。
扩展知识
在图的应用中涉及到一些其他的技术,在这里做简单的说明。
Go包text/template语法解析
包模板实现了用于生成文本输出的数据驱动模板。
模板内的数据会用{{}}包裹,{{ action }}其中的内容称为action.
action主要分为俩类内容:
- 数据的值
- 控制语句
{{ . }} .代表传入的数据 {{ .title }} 使用传入的title变量
语法介绍
{{/* comment */}} 注释
{{- content -}} 去掉俩边的空格
{{ pipeline }} 输出普通文本
{{ if pipeline }} xxx {{ else if pipeline }} xxx {{ end }} if条件语句
{{ range pipeline }} xxx {{ end }} 简单的循环语句
{{ range pipeline }} xxx {{ else }} xxx {{ end }} 条件循环语句
{{ range $index, $value := pipeline }} xxx {{ end }} 普通的循环语句
{{ define "name" }} 模板 {{ end }} 给模板命名
{{ template "name" }} 引用模板,配合define使用,可以完成模板部分的复用吧
{{ template "name" pipeline }} 条件引用模板
{{ block "name" pipeline }} 自定义模板内容 {{ end }} 使用模板name, 如果没有就使用自定义的模板内容
{{ with pipeline }} 模板1 {{ else }} 模板2 {{ end }} 一个新的上下文,如果条件不为空就模板1,否则模板2
比较运算符
eq 返回 arg1 == arg2 的布尔值
ne 返回 arg1 != arg2 的布尔值
lt 返回 arg1 < arg2 的布尔值
le 返回 arg1 <= arg2 的布尔值
gt 返回 arg1 > arg2 的布尔值
ge 返回 arg1 >= arg2 的布尔值
变量
定义变量: {{ $var = pipeline }}
变量的作用域:模板开始定义的变量作用域在整个模板,模板中块内定义的变量作用域在块内
函数
自定义函数接口:func (t *Template) Funcs(funcMap FuncMap) *Template
全局内置函数
and
{{ and .x .y .z }} xyz全部为true,返回最后一个值(z),如果任意一个为fasle,则返回它
or
{{ or .x .y .z }} xyz任意一个值为true则返回它,全为false则返回最后一个值
call
{{ call .fn .y .z } 调用fn函数传入yz参数,如果结果error不为nil, 则fatal
html 返回转义后的 HTML 字符串,这个函数不能在 html/template 中使用。
js 返回转义后的 JavaScript 字符串。
index 在第一个参数是 array、slice、map 时使用,返回对应下标的值。
index x 1 2 3 等于 x[1][2][3]。
len 返回复合类型的长度。
not 返回布尔类型参数的相反值。
print 等于 fmt.Sprint。
printf 等于 fmt.Sprintf。
println 等于 fmt.Sprintln。
urlquery 对字符串进行 url Query 转义,不能在 html/template 包中使用。
模板解析和执行
解析
引入模板,不存在就报错
func Must(t *Template, err error) *Template
从字符串new模板
func New(name string) *Template
从文件系统中查找符合匹配规则的模板
func ParseFS(fsys fs.FS, patterns ...string) (*Template, error)
加载指定的多个模板文件
func ParseFiles(filenames ...string) (*Template, error)
加载符合匹配条件的模板
func ParseGlob(pattern string) (*Template, error)
执行
//传入模板参数,执行模板,打印输出
err := tmpl.Execute(os.Stdout, "no data needed")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("execution failed: %s", err)
}
//当有加载了很多模板的时候,可以指定要执行的模板名称(T2),传入参数,执行模板,打印输出
err := tmpl.ExecuteTemplate(os.Stdout, "T2", "no data needed")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("execution failed: %s", err)
}
加载匹配的所有的模板
//go:embed tpl/*
templateDir embed.FS
var patternTmpl = []string{
"tpl/migrate/*.tpl",
"tpl/*.tpl",
}
tmpl := template.Must(template.ParseFS(templateDir,patternTmpl...))
name := "create,tpl"
data := "User"
if err := tmpl.ExecuteTemplate(b, name, data); err != nil {
log.Printf("execute template %q: %w", tmpl.Name, err)
}
在模板内使用自定义函数 funcMap
package main
import (
"log"
"os"
"strings"
"text/template"
)
func main() {
// First we create a FuncMap with which to register the function.
funcMap := template.FuncMap{
// The name "title" is what the function will be called in the template text.
"title": strings.Title,
}
// A simple template definition to test our function.
// We print the input text several ways:
// - the original
// - title-cased
// - title-cased and then printed with %q
// - printed with %q and then title-cased.
const templateText = `
Input: {{printf "%q" .}}
Output 0: {{title .}}
Output 1: {{title . | printf "%q"}}
Output 2: {{printf "%q" . | title}}
`
// Create a template, add the function map, and parse the text.
tmpl, err := template.New("titleTest").Funcs(funcMap).Parse(templateText)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("parsing: %s", err)
}
// Run the template to verify the output.
err = tmpl.Execute(os.Stdout, "the go programming language")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("execution: %s", err)
}
}
参考资料
Protocol Buffer
google 出品的一种数据交换格式, 缩写为 protobuf.
protobuf 分为编译器和运行时两部分. 编译器直接使用预编译的二进制文件即可, 可以从 releases 上下载.
protobuf 运行时就是不同语言对应的库, 以 Golang 为例:
go get github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go
语法
syntax = "proto3";
message SearchRequest {
string query = 1;
int32 page_number = 2;
int32 result_per_page = 3;
}
message 的结构非常类似于各种语言中的 struct, dict 或者 map
每个字段包括三个部分, 类型, 字段名和字段编号.
同一个 message 中字段编号应该是唯一的
注释语法是 // 和 /* ... */.
syntax = "proto3";
message Foo {
reserved 2, 15, 9 to 11;
reserved "foo", "bar";
}
message Test4 {
repeated int32 d = 4 [packed=true];
}
message SearchRequest {
string query = 1;
int32 page_number = 2;
int32 result_per_page = 3;
enum Corpus {
UNIVERSAL = 0;
WEB = 1;
IMAGES = 2;
LOCAL = 3;
NEWS = 4;
PRODUCTS = 5;
VIDEO = 6;
}
Corpus corpus = 4;
}
enum EnumAllowingAlias {
option allow_alias = true;
UNKNOWN = 0;
STARTED = 1;
RUNNING = 1; // RUNNING 是 STARTED 的别名
}
使用 reserved 注明已被废弃的字段编号和字段名称.
使用 repeated 可以指定重复字段, 即数组.
使用 enum 定义枚举类型. 每个枚举定义都必须包含一个映射值为 0 的常量作为第一个元素.可以使用 allow_alias 选项允许枚举值的别名.
syntax = "proto3";
message SearchResponse {
repeated Result results = 1;
}
message Result {
string url = 1;
string title = 2;
repeated string snippets = 3;
}
类型也可以嵌套使用.
syntax = "proto3";
import "myproject/other_protos.proto";
import public "new.proto";
使用 import 可以导入外部定义.
使用 import public 可以传递导入依赖, 通常用于被导入的 proto 文件需要更改的情况下.
protocol 编译器搜索的位置是命令行参数中的 -I/--proto_path
syntax = "proto3";
import "google/protobuf/any.proto";
message ErrorStatus {
string message = 1;
repeated google.protobuf.Any details = 2;
}
Any 类型可以让你可以在没有它们的 proto 定义时, 将 messages 用作内嵌的类型. 一个 Any 包括任意的二进制序列化的 message, 就像 bytes 类型那样, 以及用作该类型的全局唯一的标识符 URL.
syntax = "proto3";
message SampleMessage {
oneof test_oneof {
string name = 4;
SubMessage sub_message = 9;
}
}
如果你有一个 message 包括许多字段, 但同时最多只有一个字段会被设置, 可以使用 Oneof 特性来节省内存. Oneof 字段和普通的字段没有区别, 除了所有这些 Oneof 字段共享内存, 且同时只能由一个字段被设置. 你可以使用特殊的 case() 或 WhichOneof() 方法检查哪个字段被设置了, 具体方法名称取决于实现的语言.
syntax = "proto3";
map<key_type, value_type> map_field = N;
map<string, Project> projects = 3;
使用 map 可以创建关联映射.key_type 可以是 integral 或 string 类型, 即 scalar 类型中除了 floating point types 和 bytes 以外的类型. value_type 可以是除 map 以外的任何类型.
syntax = "proto3";
package foo.bar;
使用 package 可以设置命名空间, 防止 message 类型冲突. 在Golang中: package 用作 Go 包名, 除了你使用 option go_package 显式声明包名
syntax = "proto3";
service SearchService {
rpc Search (SearchRequest) returns (SearchResponse);
}
定义服务。
以上内容来自:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/92559559
相关资料
gRPC
高性能、开源的通用RPC框架,支持C#,C++,Dart,Go,Java,Kotlin,Node,Objective-C,PHP,Python,Ruby。
官方网站:https://www.grpc.io/
官方文档(Go):https://www.grpc.io/docs/languages/go/quickstart/
Protobuf生成gRPC、rest API、Swagger
安装
安装protoc
https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases
安装依赖
#protoc生成Go
go install google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go@latest
#protoc生成grpc
go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@v1.2
#protoc生成grpc gateway
go get -u github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway
#protoc生成swagger文档,之后swagger editor查看
go get -u github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-swagger
定义proto
syntax = "proto3";
package test;
import "google/protobuf/timestamp.proto";
import "google/api/annotations.proto";
option go_package = "github.com/user" ;
message User {
int32 id = 1; // Unique ID number for this person.
string name = 2;
string email = 3;
enum PhoneType {
MOBILE = 0;
HOME = 1;
WORK = 2;
}
message PhoneNumber {
string number = 1;
PhoneType type = 2;
}
repeated PhoneNumber phones = 4;
google.protobuf.Timestamp last_updated = 5;
}
// The greeting service definition.
service Gint {
// Sends a greeting
rpc FindUser (FindUserRequest) returns (FindUserResponse) {
option (google.api.http) = {
post: "/v1/user/find"
body: "*"
};
}
}
// The request message containing the user's name.
message FindUserRequest {
int32 id = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greetings
message FindUserResponse {
User user = 1;
}
生成gRPC、grpc-gateway、swagger
protoc -I. --go_out=user --go-grpc_out=user -I$(GOPATH)/pkg/mod \
-I$(GOPATH)/pkg/mod/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway@v1.16.0/third_party/googleapis \
--grpc-gateway_out=logtostderr=true:user --swagger_out=logtostderr=true:user user.proto
实现service接口,并启动服务
// 启动grpc server
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
pb "test/user/github.com/user"
)
// server is used to implement helloworld.GreeterServer.
type server struct {
pb.UnimplementedGintServer
}
// SayHello implements helloworld.GreeterServer
func (s *server) FindUser(c context.Context, in *pb.FindUserRequest) (*pb.FindUserResponse, error) {
return &pb.FindUserResponse{User: &pb.User{Name: "xixi"}}, nil
}
func main() {
flag.Parse()
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", fmt.Sprintf(":%d", 8000))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
s := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterGintServer(s, &server{})
log.Printf("server listening at %v", lis.Addr())
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
// 启动gateway server
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/runtime"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"log"
"net/http"
pb "test/user/github.com/user"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
mux := runtime.NewServeMux()
opts := []grpc.DialOption{grpc.WithInsecure()}
err := pb.RegisterGintHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, mux, "0.0.0.0:8000", opts)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
log.Println("服务开启")
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
}
查看swagger文档
生成的swagger.json如下:
{
"swagger": "2.0",
"info": {
"title": "user.proto",
"version": "version not set"
},
"consumes": [
"application/json"
],
"produces": [
"application/json"
],
"paths": {
"/v1/user/find": {
"post": {
"summary": "Sends a greeting",
"operationId": "Gint_FindUser",
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "A successful response.",
"schema": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/testFindUserResponse"
}
},
"default": {
"description": "An unexpected error response.",
"schema": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/runtimeError"
}
}
},
"parameters": [
{
"name": "body",
"in": "body",
"required": true,
"schema": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/testFindUserRequest"
}
}
],
"tags": [
"Gint"
]
}
}
},
"definitions": {
"UserPhoneNumber": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"number": {
"type": "string"
},
"type": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/UserPhoneType"
}
}
},
"UserPhoneType": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"MOBILE",
"HOME",
"WORK"
],
"default": "MOBILE"
},
"protobufAny": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"type_url": {
"type": "string"
},
"value": {
"type": "string",
"format": "byte"
}
}
},
"runtimeError": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"error": {
"type": "string"
},
"code": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32"
},
"message": {
"type": "string"
},
"details": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/protobufAny"
}
}
}
},
"testFindUserRequest": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32"
}
},
"description": "The request message containing the user's name."
},
"testFindUserResponse": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"user": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/testUser"
}
},
"title": "The response message containing the greetings"
},
"testUser": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32"
},
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"email": {
"type": "string"
},
"phones": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/UserPhoneNumber"
}
},
"last_updated": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time"
}
}
}
}
}
访问 swagger editor查看
GraphX
Spark GraphX是一个分布式图处理框架,它是基于Spark平台提供对图计算和图挖掘简洁易用的而丰富的接口,极大的方便了对分布式图处理的需求
Gorm
Golang的ORM库旨在成为开发者友好的。
全功能 ORM
关联 (Has One,Has Many,Belongs To,Many To Many,多态,单表继承)
Create,Save,Update,Delete,Find 中钩子方法
支持 Preload、Joins 的预加载
事务,嵌套事务,Save Point,Rollback To Saved Point
Context、预编译模式、DryRun 模式
批量插入,FindInBatches,Find/Create with Map,使用 SQL 表达式、Context Valuer 进行 CRUD
SQL 构建器,Upsert,数据库锁,Optimizer/Index/Comment Hint,命名参数,子查询
复合主键,索引,约束
Auto Migration
自定义 Logger
灵活的可扩展插件 API:Database Resolver(多数据库,读写分离)、Prometheus…
每个特性都经过了测试的重重考验
开发者友好
Gorm官网:https://gorm.io/zh_CN/
Gorm v2中文文档: https://learnku.com/docs/gorm/v2
安装
go get -u gorm.io/gorm
go get -u gorm.io/driver/sqlite
基于Gorm的CURD-L封装
package main
import (
"gorm.io/gorm"
"gorm.io/driver/sqlite"
)
func init() {
db, err := gorm.Open(sqlite.Open("gorm.db"), &gorm.Config{})
// 大部分 CRUD API 都是兼容的
db.AutoMigrate(&Product{})
db.Create(&user)
db.First(&user, 1)
db.Model(&user).Update("Age", 18)
db.Model(&user).Omit("Role").Updates(map[string]interface{}{"Name": "jinzhu", "Role": "admin"})
db.Delete(&user)
}
Gorm 关联的使用
创建关联,进行关联操作,以及查询关联表数据
Go代码演示
数据类型定义
type User struct {
Id int64
Name string
Address string
Phone string
Orders []*Order
}
type Order struct {
Id int64
Amount int64
CreateAt int64
Goods []*Good
UserId int64
}
type Good struct {
Id int64
Name string
Price int64
OrderId int64
}
//go run main.go
package main
import (
"gorm.io/driver/sqlite"
"gorm.io/gorm"
"gorm.io/gorm/clause"
"log"
"time"
)
//使用一对多模型创建关联
//一个用户有多个订单,一个订单有多个商品
//一个用户包含很多订单,一个订单包含很多商品
type User struct {
Id int64
Name string
Address string
Phone string
Orders []*Order
}
type Order struct {
Id int64
Amount int64
CreateAt int64
Goods []*Good
UserId int64
}
type Good struct {
Id int64
Name string
Price int64
OrderId int64
}
func main() {
//链接数据库
db, err := gorm.Open(sqlite.Open("gorm.db"), &gorm.Config{})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
//迁移表
err = db.AutoMigrate(&User{}, &Order{}, &Good{})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
//初始化关联数据
user := new(User)
user.Name = "guojinfei"
user.Address = "北京64胡同12号"
user.Phone = "15311119999"
user.Orders = []*Order{
&Order{
Amount: 1664,
CreateAt: time.Now().Unix(),
Goods: []*Good{
&Good{
Name: "雪梨",
Price: 128,
},
},
},
}
//创建数据,自动创建关联
tx := db.Create(&user)
tx = db.Save(&user)
if tx.Error != nil {
panic(err)
}
//查询关联订单数
count := db.Model(&User{Id: 2}).Association("Orders").Count()
log.Println("count:", count)
//查询用户的订单所购买的商品
var orders []Order
var goods []Good
err = db.Model(&User{Id: 2}).Association("Orders").Find(&orders)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
err = db.Model(&orders).Association("Goods").Find(&goods)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
log.Println("orders:", orders)
log.Println("goods:", goods)
//删除关联
db.Select("Orders", "Goods").Delete(&User{Id: 6})
db.Select(clause.Associations).Delete(&User{Id: 7})
}
//输出:
//count: 2
//orders: [{2 1664 1653532944 [] 2} {3 1664 1653533385 [] 2}]
//goods: [{2 雪梨 128 2} {3 雪梨 128 3}]
数据表展示
-- auto-generated definition
create table users
(
id integer
primary key,
name text,
address text,
phone text
);
-- auto-generated definition
create table orders
(
id integer
primary key,
amount integer,
create_at integer,
user_id integer
constraint fk_users_orders
references users
);
-- auto-generated definition
create table goods
(
id integer
primary key,
name text,
price integer,
order_id integer
constraint fk_orders_goods
references orders
);
Orm关联的设计提供了对关联模型的操作手段,对于关联模型的数据迁移和关联模型数据操作的一致性是需要用户去保证的
文档参考
Gorm关联 https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/belongs_to.html
实践Demo
基于以上知识的了解,接下来做一些演练。
-
实体框架设计era
受ent设计启发,设计一套完整的实体框架。使用gqlgen与前端进行数据交互,使用gorm与存储层进行数据交互。
-
一个简单的代码生成器(Gint)
Gint提供从实体到CURD-L的能力,存储层基于Gorm实现,server使用了Gin框架。
era
实体框架era (entity and relation in all)设计
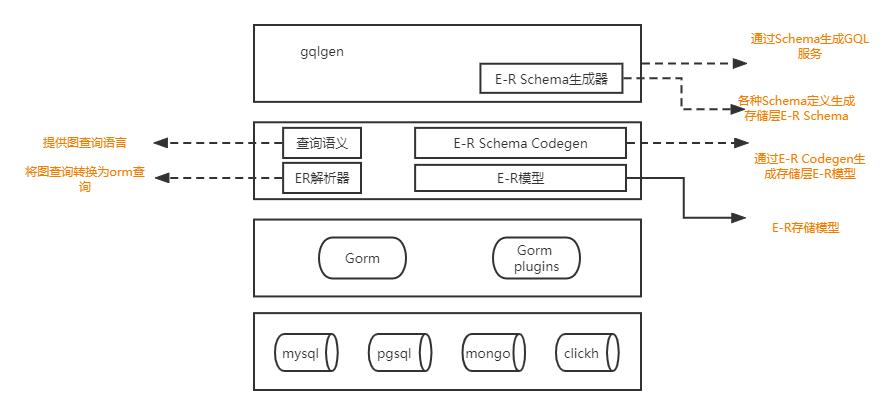
- 基于gqlgen E-R定义生成era Schema -- 参考entgql
- 基于era Schema定义生成数据E-R模型 -- 参考entc
- 提供Schema的图查询能力 -- 参考entql
- 使用Gorm操作与数据库交互 -- 参考gorm
era.大致主要包含一下四个部分:
Schema 生成器(erac)
用户通过Schema生成器的定义语言定义Schema的实体、边、属性、注解等内容。 经由Schema生成器生成多种协议的实体和关系的抽象,进一步生成各种图查询的实体和关系的协议,例如gqlgen的schema协议。
操作步骤:
- 定义实体
- 执行
shell go generate ./...生成实体-关系抽象,同时生成指定的schema协议(例如gqlgen schema定义)
GraphQL server(eragql)
通过erac生成gqlgen schema,使用gqlgen对外提供GraphQL服务
执行步骤:
- 定义实体
- 执行
shell go generrate ./...生成代码和服务 - 实现服务接口 (使用eraql)
- 运行服务
图数据库查询语言 (eraql)
gorm兼容了多种数据库驱动。eraql是基于gorm实现的数据库图查询语言。
操作步骤:
- 链接数据库
- 完成数据库迁移 (实体-关系模型到数据表的映射)
- 执行图查询
存储层实体-关系模型(era)
基于erac生成的实体-关系抽象 基于eraql图查询语言 结合实体框架模板 生实体框架代码
操作步骤:
- 通过erac定义实体
- 执行
shell go generate ./...生成实体-关系存储层方法 - 链接数据库、完成数据迁移、执行图查询
实体关系在数据库表和Go数据类型中的表现形式
通过对ent的学习,我们了解到实体关系大致分了八个模式
那么这些实体关系是如何在数据表和数据类型定义中体现的呢
ent实体框架中的边(关系或实体之间的关联)
- 1对1
- 1对1 自引用
- 1对1 双向自引用
- 1对多
- 1对多 自引用
- 多对多
- 多对多 自引用
- 多对多 双向自引用
自引用和双向自引用在数据结构是其实一样的,它是对于有向图来说
我们暂时只针对无向图,在数据存储结构上来说,其实分为一对一、一对多和多对多。
在数据表中的表现形式
在数据表存储时,使用数据表外键(foreign key)来表示实体之间的关联关系
- 一对一
TODO
- 一对多
TODO
- 多对多
TODO
在Go数据类型中的表现形式
在Go数据类型中,使用结构体类型字段表示数据库外键,以及数据关联模型的引用
- A属于B
// `User` 属于 `Company`,`CompanyID` 是外键
type User struct {
gorm.Model
Name string
CompanyID int
Company Company
}
type Company struct {
ID int
Name string
}
- A包含B
// User 有一张 CreditCard,UserID 是外键
type User struct {
gorm.Model
CreditCard CreditCard
}
type CreditCard struct {
gorm.Model
Number string
UserID uint
}
- A包含很多B
// User 有多张 CreditCard,UserID 是外键
type User struct {
gorm.Model
CreditCards []CreditCard
}
type CreditCard struct {
gorm.Model
Number string
UserID uint
}
- 多对多
// User 拥有并属于多种 language,`user_languages` 是连接表
type User struct {
gorm.Model
Languages []*Language `gorm:"many2many:user_languages;"`
}
type Language struct {
gorm.Model
Name string
Users []*User `gorm:"many2many:user_languages;"`
}
存在关联表 user_languages;
一个简单的代码生成器(Gint)
Gint提供从实体到CURD-L的能力,存储层基于Gorm实现,server使用了Gin框架。
Gint初始化
新建项目
go mod init ginttest
cd ginttest
go mod tidy
执行Gint初始化,可以方便的得到一个Schema定义的框架。
go run gitee.com/wennmu/gint.git init
生成的代码目录:
--gint
----gint.yml // schema定义文件
----generate.go // 生成代码脚本
定义实体以及边
在gint.yml配置文件中增加实体定义
varsion: 1
schemas:
- name: User
fields:
- name: name
ftype: string
anno:
- name: Addr
ftype: string
anno:
- name: Phone
ftype: string
anno:
edges:
- from: Team
to: Order
mode: 2
生成代码
执行命令生成schema的代码。
go generate ./...
启动服务
新建main.go添加如下代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"ginttest/gint"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"gorm.io/driver/sqlite"
"gorm.io/gorm"
"log"
)
func main() {
db, err := gint.Open(sqlite.Open("gint.db"), &gorm.Config{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("open db err")
}
if err = db.CreateMigrate(); err != nil {
log.Fatal("migrate err")
}
r := gin.Default()
gint.RegisterGintRouter(r, "api", func(c *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println("中间件")
c.Next()
})
err = r.Run(":8000")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
return
}
}
Gint仓库
Github: github.com/wennmu/gint.git
Gitee: gitee.com/wennmu/gint.git
安装
从这里下载GitHub Releases page
命令行工具
mdbook命令行工具用于创建和构建图书。安装mdbook后,可以在终端执行mdbook help命令查看可用的命令。
下面的部分提供了关于不同命令的深入信息。
mdbook init <directory> — Creates a new book with minimal boilerplate to start with.
mdbook build — Renders the book.
mdbook watch — Rebuilds the book any time a source file changes.
mdbook serve — Runs a web server to view the book, and rebuilds on changes.
mdbook test — Tests Rust code samples.
mdbook clean — Deletes the rendered output.
mdbook completions — Support for shell auto-completion.
配置
[output.html]
# theme = "my-theme"
default-theme = "Coal"
# preferred-dark-theme = "navy"
# curly-quotes = true
# mathjax-support = false
# copy-fonts = true
# # additional-css = ["custom.css", "custom2.css"]v
# # additional-js = ["custom.js"]
# no-section-label = false
# git-repository-url = "https://github.com/rust-lang/mdBook"
# git-repository-icon = "fa-github"
# edit-url-template = "https://github.com/rust-lang/mdBook/edit/master/guide/{path}"
# site-url = "/example-book/"
# cname = "myproject.rs"
# input-404 = "introdution.md"
目录的创建
# Summary
[Introduction](README.md)
# User Guide
- [Installation](guide/installation.md)
- [Reading Books](guide/reading.md)
- [Creating a Book](guide/creating.md)
# Reference Guide
- [Command Line Tool](cli/README.md)
- [init](cli/init.md)
- [build](cli/build.md)
- [watch](cli/watch.md)
- [serve](cli/serve.md)
- [test](cli/test.md)
- [clean](cli/clean.md)
- [completions](cli/completions.md)
- [Format](format/README.md)
- [SUMMARY.md](format/summary.md)
- [Draft chapter]()
- [Configuration](format/configuration/README.md)
- [General](format/configuration/general.md)
- [Preprocessors](format/configuration/preprocessors.md)
- [Renderers](format/configuration/renderers.md)
- [Environment Variables](format/configuration/environment-variables.md)
- [Theme](format/theme/README.md)
- [index.hbs](format/theme/index-hbs.md)
- [Syntax highlighting](format/theme/syntax-highlighting.md)
- [Editor](format/theme/editor.md)
- [MathJax Support](format/mathjax.md)
- [mdBook-specific features](format/mdbook.md)
- [Markdown](format/markdown.md)
- [Continuous Integration](continuous-integration.md)
- [For Developers](for_developers/README.md)
- [Preprocessors](for_developers/preprocessors.md)
- [Alternative Backends](for_developers/backends.md)
-----------
[Contributors](misc/contributors.md)
详细说明请参考说明文档